Caffeine Energy Gum: A Convenient Way to Boost the Metabolism and Burn Fat
January 9, 2023
Caffeine is a stimulant that is found in many foods and beverages, including coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks. It is also found in some medications and supplements. Caffeine is known to have a number of effects on the body, including increasing alertness, improving concentration, and boosting energy levels.
One of the ways in which caffeine can affect the body is by increasing the metabolism. The metabolism is the process by which the body converts food into energy. When the metabolism is accelerated, the body is able to burn calories more efficiently, which can help to promote weight loss.
Several studies have shown that caffeine can increase the metabolism and help the body burn fat. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that caffeine consumption was associated with a higher metabolic rate in both lean and obese individuals. Another study, published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition, found that caffeine consumption increased fat oxidation (the breakdown of fat) in men.
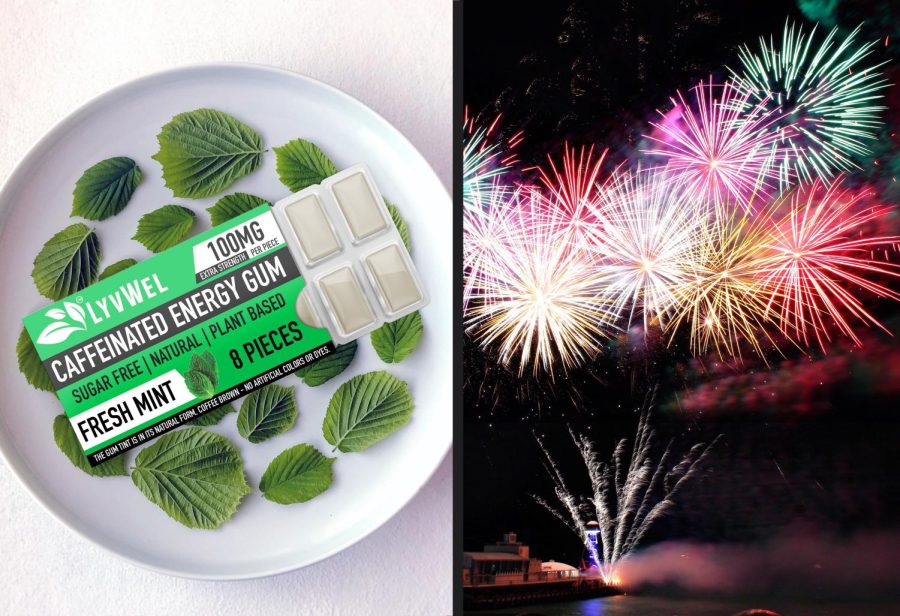
Caffeine energy gum is a type of chewing gum that contains caffeine and is marketed as a way to increase energy and focus. While the research is limited on the long term effectiveness of caffeine in chewing gum specifically, it is likely that the caffeine in the gum would have similar effects on the body as caffeine from other sources. Especially since the absorption rate of caffeine by chewing it is much faster. Also caffeinated chewing gum contains almost no calories and no carbs. In comparison to energy drinks or coffee products like a cappuccino, it eliminates roughly 75 calories every time you have a caffeine craving. Lowering your calorie count weekly has been linked to weight loss.
It is important to note that while caffeine can increase the metabolism and help the body burn fat, it is not a magic solution for weight loss. A healthy diet and regular physical activity are still essential for maintaining a healthy weight. In addition, consuming too much caffeine can have negative side effects, such as insomnia, jitters, and an increased heart rate. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation and to consult with a healthcare professional before adding caffeine to your diet.
It is also worth noting that the effects of caffeine on the metabolism may vary from person to person. Some people may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and may experience an increase in their metabolism after consuming small amounts, while others may need to consume larger amounts in order to see a noticeable effect.
Additionally, the effects of caffeine on the metabolism may decrease over time as the body becomes accustomed to it. This is known as tolerance, and it means that the body becomes less sensitive to the effects of caffeine. As a result, it may be necessary to increase the amount of caffeine consumed in order to continue to see the same benefits.
It is also important to consider the source of caffeine when trying to increase the metabolism and burn fat. Some sources of caffeine, such as coffee and tea, can provide additional health benefits, as they are rich in antioxidants and other beneficial compounds. On the other hand, energy drinks and some supplements may contain added sugars and other ingredients that can contribute to weight gain.
In addition to its effects on the metabolism, caffeine may also have other benefits for weight loss. For example, it can help to reduce appetite and cravings, making it easier to stick to a healthy diet. It may also improve physical performance, allowing people to exercise more effectively and burn more calories.
Overall, caffeine has been shown to have a number of effects on the body, including increasing the metabolism and helping the body burn fat. Caffeine energy gum provides some of the same benefits without the additional calories intake as compared other sources of caffeine and makes it one of the best alternative caffeine products.
Sources that were used for this article:
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: “Caffeine intake increases the rate of energy expenditure and fat oxidation in lean and obese women.”
Journal of the American College of Nutrition: “The effects of caffeine ingestion on NE kinetics, fat oxidation, and energy expenditure in younger and older men.”
Mayo Clinic: “Caffeine: How much is too much?”
Harvard Health Publishing: “The truth about caffeine”