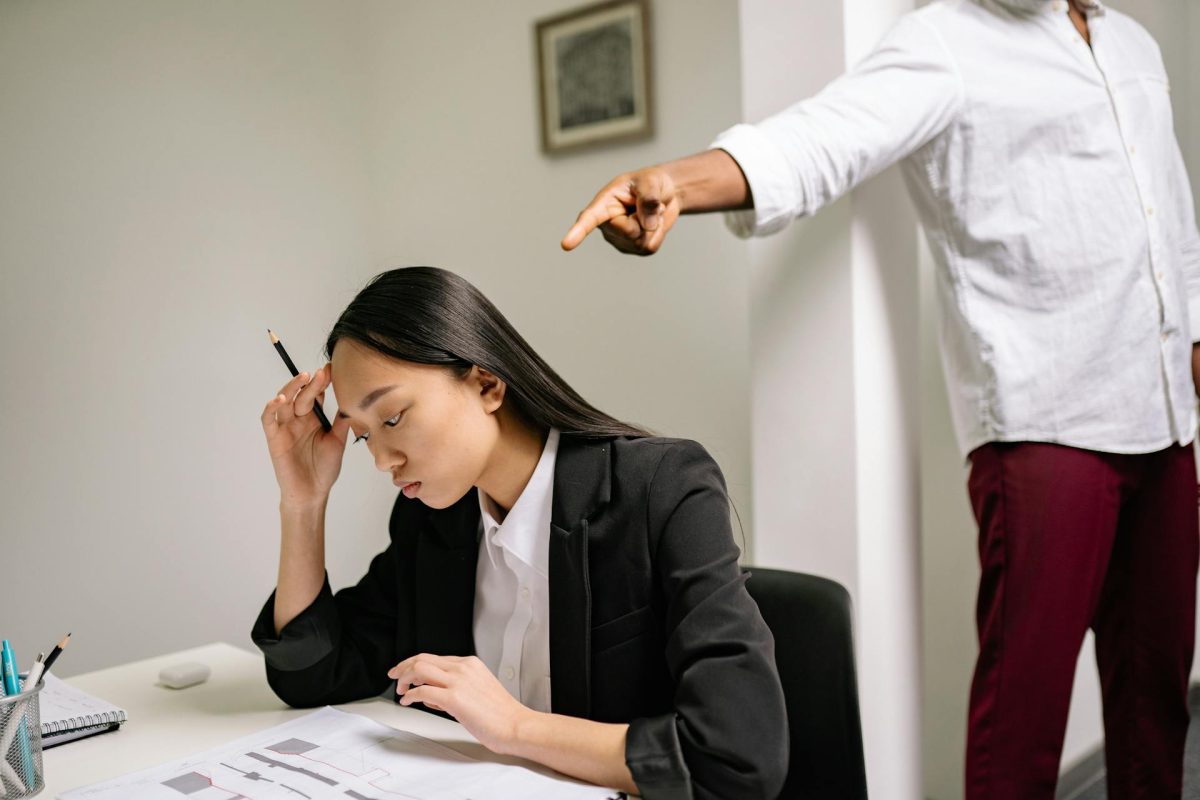
Workplace discrimination is, unfortunately, a common experience for many employees across the United States. According to a recent report, nearly 91% of individuals in the U.S. have encountered some form of discrimination at work, whether based on race, gender, age, religion, or disability. These statistics are not only shocking but highlight how critical it is for employees to be well-versed in their rights and the legal steps available to them. If you find yourself in a situation where you’re being treated unfairly due to who you are, knowing how the law can help you is essential.
This guide will help you understand the steps you can take if you’re facing workplace discrimination, empowering you to protect your rights and seek justice.
1. Understand What Qualifies as Discrimination
The first step in tackling workplace discrimination is to clearly understand what qualifies as such. Discrimination occurs when an employer treats an employee unfavorably because of a protected characteristic, such as race, gender, religion, disability, national origin, or age. These actions can manifest in a variety of ways. These might include unequal pay, wrongful termination, exclusion from opportunities, or even verbal or physical harassment.
It’s important to educate yourself on the legal definitions of discrimination under federal laws such as the Civil Rights Act and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act. If your experience falls under these categories, then you may have a strong case for legal recourse.
2. Hire an Expert Employment Lawyer
One of the most important decisions you’ll make if you’re facing discrimination is hiring an experienced employment lawyer. Discrimination cases can be complex, and only an expert can help you understand all the legal nuances. A lawyer specialized in employment law will have a deep understanding of discrimination regulations and can advise you on the strength of your case.
When selecting a lawyer, consider their experience, especially with cases similar to yours. It’s also a good idea to check reviews, testimonials, and their success rate in handling discrimination cases. An experienced lawyer will help you gather the necessary evidence, file complaints with the appropriate agencies, and represent you in negotiations or court proceedings. Having a legal expert on your side will increase your chances of receiving a fair and just resolution.
3. Document Every Incident Thoroughly
Detailed documentation is a key component in building a strong discrimination case. Begin by keeping a personal record of every discriminatory incident. Include details such as the date, time, location, individuals involved, and a clear description of what transpired. If possible, secure witnesses who can support your account of the incidents. Also, save any written communications (such as emails, text messages, or memos) that provide evidence of unfair treatment or discriminatory behavior.
Having a comprehensive, organized record of these events will be crucial when presenting your case to an employment lawyer, HR, or the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
4. Report the Discrimination Internally First
Before taking external legal action, it’s typically advisable to report the discrimination within your organization. Most companies have policies and procedures for handling discrimination complaints. Filing an internal complaint demonstrates that you attempted to resolve the issue through the company’s established channels. When filing your complaint, be sure to present all the documentation you’ve gathered. If your company fails to take appropriate action or retaliates against you, that will only strengthen your case when you move forward with legal steps.
5. File a Complaint with the EEOC
If internal attempts to resolve the issue fail or your employer doesn’t address the discrimination adequately, filing a formal complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is the next critical step. The EEOC is a federal agency responsible for making sure that anti-discrimination laws are not adhered to at every workplace. Filing a complaint allows the EEOC to investigate your claim.
You must file your complaint within a specific time frame, typically within 180 days of the discriminatory incident. However, this deadline can be extended to 300 days if your state has its own anti-discrimination laws that apply to your case. The EEOC will review your complaint and, if they find merit, may either pursue legal action on your behalf or issue a “right to sue” letter, which allows you to file a lawsuit independently.
6. Be Prepared for Possible Retaliation
Filing a discrimination complaint can sometimes lead to retaliation from your employer. Retaliation may take various forms, such as demotion, reduction in hours, exclusion from projects, or even wrongful termination. It’s important to know that retaliation is illegal under federal and state laws. Employers are not allowed to punish you for exercising your right to report discrimination.
If you experience retaliation, document these actions carefully, just as you would with the original incidents of discrimination. This documentation will help support any additional claims you need to file. Retaliation complaints can also be submitted to the EEOC. Make sure your lawyer is with you during these stages, as they can advise you on how to handle retaliation and protect your rights.
7. Consider Mediation or Settlement
Not all discrimination cases end up in court. In many instances, disputes are resolved through mediation or settlement. Here, a neutral third party will help both you and your employer negotiate a solution. It’s often less stressful, more affordable, and quicker than a full legal trial.
During mediation, you and your employer will discuss potential resolutions, which might include monetary compensation, job reinstatement, or changes to workplace policies. While settlement is a faster resolution, your lawyer will help you determine whether settling is the best option for your case.
8. Prepare for Legal Action if Necessary
If mediation doesn’t resolve the issue and the discrimination continues, you may need to prepare for legal action. Filing a lawsuit can be a lengthy and complex process, but it may be necessary to achieve justice. Your lawyer will guide you through each step, from filing the lawsuit to presenting your case in court.
Lawsuits often involve depositions, the collection of evidence, and negotiations between legal teams. Throughout this process, you must stay organized and provide your lawyer with all relevant documentation. Having a strong case backed by thorough evidence will increase your chances of success.
9. Stay Informed and Advocate for Policy Changes
While fighting your case is vital, it’s also important to stay informed about broader legal trends and advocate for changes that could help prevent discrimination in the future. Many individuals who have successfully fought discrimination cases go on to support workplace diversity initiatives or policy reform efforts. By staying informed, you can help create a more equitable work environment for others.
Taking action against workplace discrimination is more than just a step toward justice for yourself; it’s a powerful move that challenges a system allowing unfair treatment to persist. Standing up for your rights sends a message that no one should endure discrimination based on who they are. It’s not an easy journey, but it’s a courageous move that can inspire change, not just in your workplace but also in the broader culture of fairness and equality.